
Cannabinoids like THCV and THC are among the most notable compounds derived from the cannabis plant. While both share some similarities, they exhibit unique properties that set them apart.
THCV and THC interact differently with the body, producing distinct psychoactive properties and potential benefits.
In this article, we’ll delve into the nuances of THCV vs THC. We’ll explore how these cannabinoids contribute to the broader spectrum of effects associated with cannabis sativa.
The cannabis plant produces a variety of compounds, commonly referred to as cannabinoids. Among these, THC has long been known for its psychoactive effects, making it a key player in both medical or recreational use.
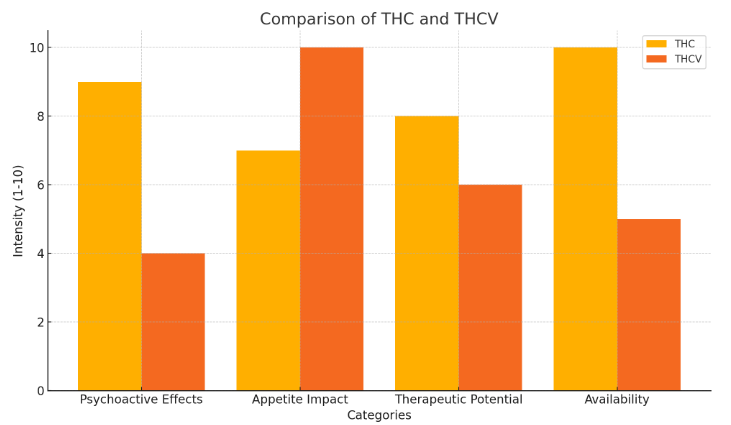
On the other hand, THCV has unique potential. It may suppress appetite and help with weight management.
Knowing the key differences between THCV and THC can help consumers choose cannabis products and their uses.
THCV and THC differ in terms of molecular structure, psychoactive properties, and how they interact with the endocannabinoid system. These differences result in varied effects, such as THC’s ability to stimulate appetite versus THCV’s reputation for potentially suppressing appetite.
Despite their differences, both cannabinoids are derived from the same plant. Both contribute to its diverse range of effects.
This blog will explore these cannabinoids’ unique properties in-depth, breaking down their potential benefits while avoiding unproven claims.
Read on to uncover how THCV and THC stack up in terms of psychoactivity, therapeutic applications, and consumer appeal.
One of the most notable differences between THCV and THC lies in their molecular structure. Both are cannabinoids from the cannabis plant. Their chemical compositions set them apart.
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is formed when the precursor THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) undergoes decarboxylation. Similarly, THCV, or tetrahydrocannabivarin, is derived from THCVA (tetrahydrocannabivarinic acid) through a similar process.
The differences in structure between these two cannabinoids affect how they interact with the body’s cannabinoid receptors. For instance, THC primarily binds with CB1 receptors, leading to its well-known “high” effects.
THCV, however, interacts differently. At low doses, it acts as a neutral antagonist to CB1 receptors. This contributes to its unique properties, like appetite suppression.

The production of cannabinoids like THCV and THC begins with the biosynthesis of common precursors in the cannabis plant. These include geranyl pyrophosphate and olivetolic acid. They combine to form cannabigerolic acid (CBGA).
CBGA then branches into various pathways, creating cannabinoids such as THCA and THCVA. Interestingly, the production of THCV is often associated with specific cannabis strains that have been bred to express higher levels of THCVA.
Strains rich in THCV are typically found in landrace varieties of cannabis sativa from regions such as Africa and Asia.
While THC dominates most modern cannabis products, THCV remains a rarer cannabinoid due to its limited expression in many cannabis plants.
This rarity has spurred interest in cultivating strains specifically bred for higher THCV content. The different biosynthetic pathways create the varied effects of THCV and THC. They also show the cannabis plant’s complex chemistry.
By understanding the foundational differences in structure and production, it becomes clearer why THCV and THC produce such varied outcomes when consumed.
In the next section, we’ll explore how these cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system to produce their respective feel-good effects.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a vital regulatory network in the human body, consisting of receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes. Both THCV and THC affect this system. But, they interact with cannabinoid receptors—specifically CB1 and CB2—differently.
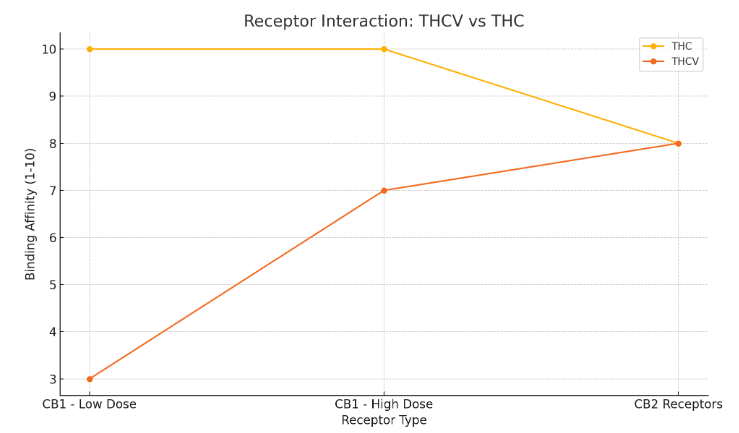
THC is widely recognized for its ability to bind strongly with CB1 receptors, predominantly located in the brain and central nervous system. This interaction is what produces THC’s psychoactive effects, including the well-known “high.”
In contrast, THCV has a dual relationship with CB1 receptors. At lower doses, THCV acts as a CB1 antagonist, which may contribute to its ability to suppress appetite. At higher doses, however, it can switch roles and act as a CB1 agonist, producing mild psychoactive effects.
THCV also engages with CB2 receptors in the immune system, although research into these interactions is still developing.
One of THCV’s unique properties is its role in modulating the ECS without the intense psychoactivity typically associated with THC. This characteristic has drawn attention to THCV for its potential in areas like weight management and metabolic regulation.
Early cannabis research suggests that THCV may help regulate lipid and glucose metabolism by influencing CB1 receptor activity. More research is needed to confirm these findings.
THC’s psychoactive properties are often described as euphoric, relaxing, and even sedative, depending on the strain and dosage.
On the other hand, THCV produces much subtler effects. At high doses, THCV can cause mild psychoactivity. But, it is often called a “functional cannabinoid.” It promotes focus and clarity without THC’s intense high.
Key Differences in Receptor Interaction
These distinct mechanisms highlight why THCV vs THC appeal to different consumer preferences.
In the following section, we’ll explore their potential benefits and why consumers may choose one cannabinoid over the other.
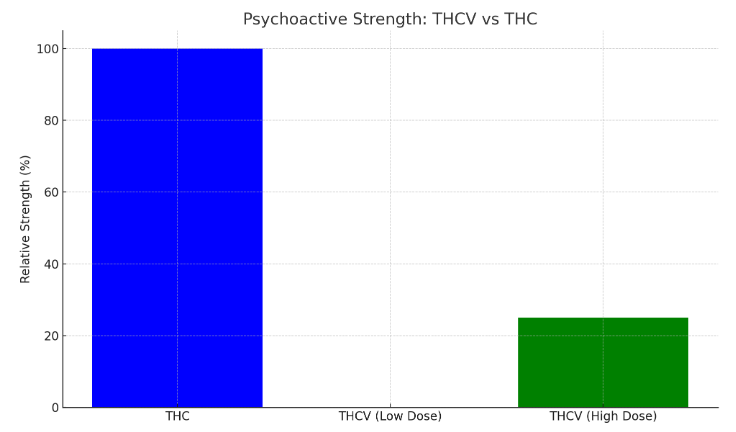
THCV is about 25% as strong as THC in terms of psychoactive effects. While THC binds strongly to CB1 receptors, creating a powerful “high,” THCV has a much milder effect.
At low doses, THCV blocks CB1 receptors and doesn’t cause any psychoactivity. At higher doses, it activates these receptors but produces only a light, focused effect compared to THC’s full-strength euphoria.
Both THCV and THC are popular for their potential benefits. But, their effects and uses differ greatly. THC is well-known for its psychoactive effects and has been widely explored for medicinal benefits such as pain relief, appetite stimulation, and relaxation.
THCV, on the other hand, is gaining attention. It has unique, focus-related, appetite-suppressing effects.
Related Article: THCV Effects: A Consumer’s Guide
While THC is well-suited for those seeking relaxation or relief, THCV appeals to individuals looking for an energizing, functional experience. Both cannabinoids have a place in the growing cannabis market. They offer diverse options for different consumer needs.
Like all cannabinoids, THCV and THC have potential side effects, though they vary in intensity and scope. THC’s well-documented side effects include temporary memory impairment, dry mouth, and increased heart rate, particularly with high doses.
THCV’s safety profile is less established but is generally considered milder. As a CB1 receptor antagonist at low doses, THCV may not produce the intense psychoactive feelings associated with THC. However, at higher doses, it may lead to subtle euphoria, and further research is needed to fully understand its long-term safety.
The legal status of THC and THCV varies depending on the region. THC, as the primary psychoactive component of cannabis, is regulated in most countries, with availability often limited to medical cannabis or recreational use where permitted.
THCV, by contrast, is less widely available, but its increasing popularity has spurred the development of strains and products specifically targeting this cannabinoid.
In regions where cannabis sativa and hemp-derived cannabinoids are legal, THCV is emerging as a sought-after option in wellness-focused markets.

When it comes to THCV vs THC, the choice ultimately depends on individual preferences and needs. THC is a classic cannabis staple. It relaxes and has psychoactive effects. This made it popular in both medical and recreational markets. THCV, on the other hand, provides an alternative for those seeking focus, clarity, or appetite suppression.
As cannabis research continues to uncover new insights, both cannabinoids will likely play pivotal roles in the evolving world of cannabis products.
Whether you’re exploring the energizing potential of THCV or the calming effects of THC, these cannabinoids highlight the incredible diversity of the cannabis plant.
For consumers curious about the key differences between these cannabinoids, it’s worth exploring the growing variety of products designed to showcase their unique effects. Always opt for lab-tested, high-quality cannabis products from Hollyweed to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience.